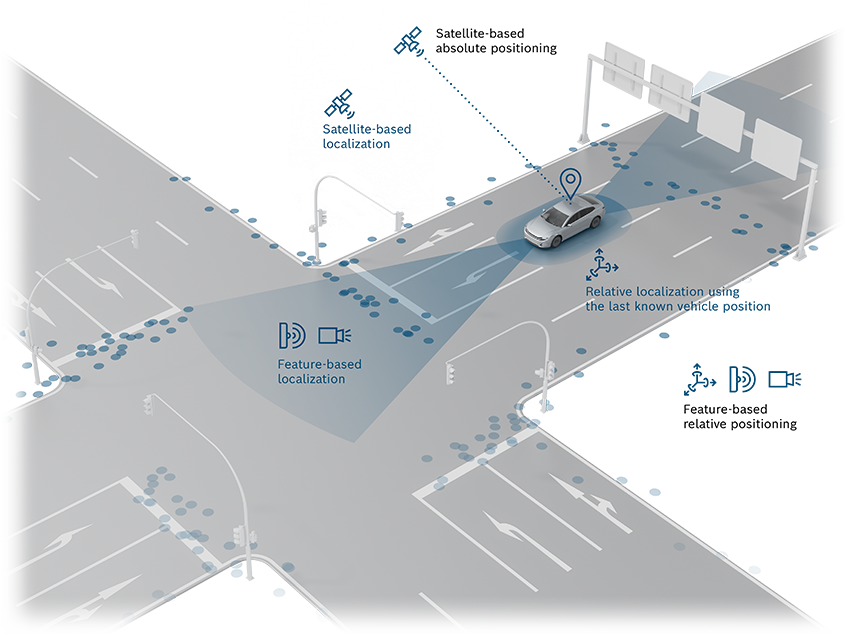
To achieve highly accurate, reliable localization, multiple technologies are used: surround sensors, satellite navigation, and inertial sensor systems.
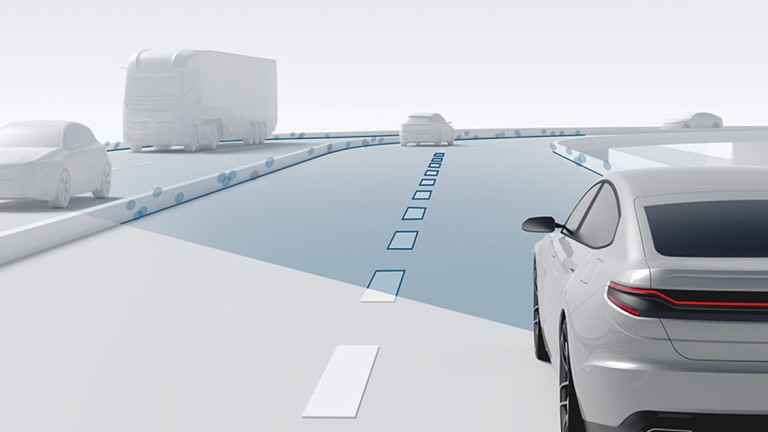
Bosch utilizes data collected by the surround sensors in the vehicle to create an independent map layer that depicts the unique features of the road, known as the localization map . Radar and camera sensor systems and the fusion of their data provide important information on objects in the vehicle’s surroundings. To satisfy the stringent safety requirements of assisted and automated driving, advanced satellite-based localization is used alongside surround sensors and the road signature. The vehicle localization system from Bosch plays a key role in this.
In addition to external GNSS signals (GPS, GAL, BOS), it uses a correction service to improve satellite positioning and combines information from sources including the inertial measurement system to output a reliable position calculation. The Inertial measurement unit is used when features in the surroundings are insufficient or the satellite connection is disrupted. In this case, the system calculates the relative change in position of the vehicle using sensor information, which allows localization to remain active. In bringing these features together, Bosch offers a package of hardware, software, and services for reliable localization that forms a self-contained redundant system to precisely determine the position of the vehicle.